Rockwell ControlLogix 5580: When Sources Diverge, DeviceTotal Delivers Actionable Truth

Rockwell ControlLogix 5580: When Sources Diverge, DeviceTotal Delivers Actionable Truth In the oil & gas industry, every hour of downtime translates into lost production and compliance risk. Critical OT assets like Rockwell ControlLogix 5580 controllers are deployed across refineries, pipelines, and offshore platforms. When these devices run outdated firmware, a single overlooked vulnerability can cascade into safety risks, regulatory exposure, and multimillion-dollar operational losses. One such case involved firmware v32.011. Rockwell’s own advisory confirmed this version as affected by CVE-2024-6077. Yet in public vulnerability records, the issue was listed under GuardLogix, not ControlLogix. For operators cataloguing devices as ControlLogix, this mismatch meant production controllers appeared secure in scans, even though they were not. The result: a dangerous false negative at scale, leaving critical infrastructure exposed. Without DeviceTotal With DeviceTotal 🟥 Missed vulnerability due to CPE mismatch 🟩 CVE-2024-6077 correctly mapped to ControlLogix 5580 / 32.011 🟥 No precise fix surfaced 🟩 Vendor-confirmed remediation path (corrected in later versions per Rockwell SD1693) 🟥 Non-compliant reporting and delayed patching 🟩 Daily risk scoring aligned with vendor disclosure 🟥 Reliance on NVD CPEs only 🟩 Auditable provenance (Rockwell SD1693 + NVD entry) The Security Gap Device in Use: Rockwell ControlLogix 5580 1756-L83E Firmware: 32.011 Search Source: NVD / conventional scanner Result: CVE-2024-6077: the 32.011 firmware was listed only under GuardLogix 5580 CPE, not ControlLogix 5580. The public database lists version 33.011 as the first affected version for devices in the ControlLogix 5580 series. For oil & gas OT environments, where devices are catalogued as ControlLogix, the vulnerability went unflagged. The result: safety-critical systems falsely reported as secure. According to NVD, the ControlLogix 5580 32.011 is not vulnerable to CVE-2024-6077 The Reality Found by DeviceTotal DeviceTotal aligned Rockwell’s advisory with real-world asset data: Vendor: Rockwell Automation Advisory Link: Rockwell Security Advisory SD1693 Affected Device: ControlLogix 5580 (1756-L83E) Firmware: First affected in v32.011, remediated in later versions Status: Public record published, but misaligned in device mapping DeviceTotal Value: Unified vendor and public data, closing the false negative gap for ControlLogix assets in oil & gas networks A screenshot from the Rockwell official advisory marking the v.32.011 vulnerable to CVE-2024-6077 Actionable Insights Platform View – Workarounds: For each vulnerability, GE advises restricting physical access and applying standard cybersecurity best practices. For example, CVE-2024-6077 includes a vendor-recommended workaround that eliminates the vulnerability if the CIP security is disabled. Platform View – Upgrade Path: For running firmware 32.011, the latest vendor version available is 37.012, providing reduction of the risk score. As for the CVE-2024-6077, it is remediated by upgrading to 33.017 and later versions. Outcome Thanks to DeviceTotal, the security team was able to: Correctly identify ControlLogix 32.011 as vulnerable Plan upgrades within scheduled maintenance windows Maintain compliance with vendor-aligned evidence Eliminate blind spots caused by data mismatches across sources How DeviceTotal Integrates with Oil & Gas OT Security Teams Asset Inventory AlignmentFragmented inventories (ControlLogix vs. GuardLogix classifications) are normalized, ensuring OT teams see the true risk profile. Compliance & Regulatory ReportingFrameworks such as NERC CIP, IEC 62443, and NIS2 require vendor-verified vulnerability data. DeviceTotal provides audit-ready evidence, tied directly to Rockwell advisories. Incident Response ReadinessDuring incidents, SOC and OT teams need firmware-exact intelligence to decide which controllers to patch or isolate. DeviceTotal delivers this without disrupting production. Lifecycle & ProcurementWith 10–20 year lifecycles common in oil & gas, DeviceTotal tracks EoL/EoS and vendor patch visibility to help avoid long-term hidden risks. Why It Matters? At the scale of oil & gas operations, even small misalignments between vendor advisories and public records can cause: False negatives that slip through large-scale asset inventories Compliance blind spots when reports show devices as secure but aren’t Escalating downtime costs when vulnerabilities are missed in critical systems Risk to safety and regulatory standing across production networks DeviceTotal aggregates all intelligence sources — vendor and public — into a single, definitive truth.
Case Study: GE Healthcare LOGIQ E10 — GE Missed Vulnerabilities on Their Own Device. DeviceTotal didn’t.
Hospitals depend on vendor advisories to know if their devices are exposed. But what happens when the vendor’s own data is incomplete?
Bridging the CVE Gap: Why Organizations Can’t Rely on NVD Alone — and How DeviceTotal Closes It
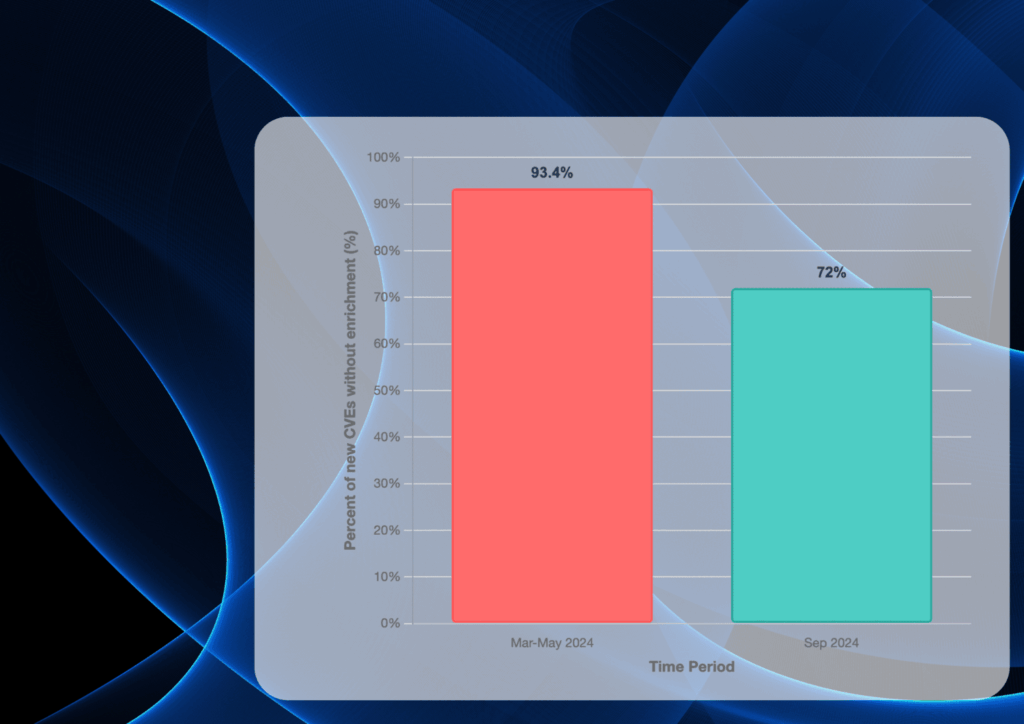
Bridging the CVE Gap: Why OEMs Can’t Rely on NVD Alone — and How DeviceTotal Closes It Forget half-measures — DeviceTotal is redefining device risk intelligence with unmatched accuracy and speed. Here are four standout wins from countless success stories: On Cisco IOS 15.9(3)M3, DeviceTotal mapped 31 CVEs—35 % more than NVD’s 23 — and instantly resolved 24 CPE misassignments (77 % false negatives/false positives), versus NVD’s four-month correction lag. JTEKT PC10PE-1616P (JVN and NVD): Public feeds reported 3 CVEs; DeviceTotal found 5 — a 66 % uplift. These vulnerabilities are still missing from JVN/NVD. Fortinet FortiGate 200F: NVD missed CVE-2025-22862 entirely; DeviceTotal surfaced it on disclosure, delivering 4.3 % more CVEs with full remediation guidance. This vulnerability is still missing from the NVD. These highlights are just the tip of the iceberg. With 100 % vulnerability coverage, insights from the day of disclosure, and rich operational context — EoL dates, vendor-recommended remediation and mitigation, latest versions, and actionable insights — DeviceTotal empowers you to remediate faster, smarter, and with absolute confidence. Capability NVD DeviceTotal Advantage Vulnerabilities Covered ~50–60 % of firmware CVEs ✅ 100 % of vendor disclosures (incl. non-CVE advisories) +40 – 50 percentage points uplift Extra vulnerabilities beyond public feeds 0 % ✅ 100 % (e.g. +2 JVN CVEs, CVE-2025-22862) Reveals hidden vulnerabilities CPE Mismatch Resolution 1 to 4 months or longer ✅ Resolves 100 % of misassignments Eliminates blind spots False Negatives 4.2 – 25.8 % (case-study range) 0 % No missed exposures False Positives Up to 77.4 % 0 % No wasted triage What Organizations Get Beyond Data Available on NVD and Other Public Databases Even when NVD lists a CVE, it typically does not provide the operational context organizations need to act quickly and correctly. DeviceTotal adds the missing, vendor‑aligned layers. Capability NVD DeviceTotal Advantage EoL/Lifecycle ❌ ✅ +40 – 50 percentage points uplift Mitigation/Workaround links ~ (sporadic) ✅ Reveals hidden vulnerabilities Fixed-firmware mapping ❌ ✅ Eliminates blind spots Normalized risk ~ (partial) ✅ No missed exposures Prioritization Up to 77.4 % ✅ No wasted triage Time-to-insight 60-120 days From the moment of vendor disclosure Instant actionable insights The problem: NVD enrichment backlog → systematic mapping errors Over 2024–2025, a large share of CVEs entered the NVD without enrichment (no CVSS, no CPE product mappings, and often marked “Awaiting Analysis”), and many stayed that way for months. Independent measurements found that 93.4% of CVEs published after Feb 12, 2024 were still unanalyzed as of May 19, 2024; by Sept 21, 2024, 72.4% (≈18,358 CVEs) remained unanalyzed, including 46.7% of Known‑Exploited CVEs. FIG-1: NVD Backlog Indicators: The bars show the share of new CVEs lacking NVD analysis (i.e., missing CVSS, CPE, or marked Awaiting Analysis). When these fields are absent or late, device/firmware matching breaks, yielding the misses and mis‑mappings seen in the case studies. While NVD hasn’t published an official 2025 percentage, NIST’s March 19, 2025 update confirmed processing had resumed but the backlog was still growing, and contemporaneous reporting put the queue at roughly 25,000 unprocessed CVEs in March 2025. DeviceTotal Case Studies Prove NVD’s Coverage Gaps Public feeds fall short. Missing CPEs, analysis delays, and version mismatches in NVD create critical blind spots and generate false positives, hampering device teams’ ability to act. DeviceTotal delivers exact device risk intelligence, updated daily directly from vendors. Across every case, we achieved 100 % recall and provided the operational context — official EoL timelines, vendor-verified mitigations, fixed-firmware mappings, normalized risk scores, and prioritized actions. Case study A — Eliminating Blind Spots for Cisco IOS 15.9(3)M3 While NVD took four months (Feb 5–Jul 2, 2025) to correct its mappings, DeviceTotal instantly flagged 31 CVEs on IOS 15.9(3)M3 — including 24 CPE misassignments (77 % false negatives on the correct train and 77 % false positives on the wrong one). Where NVD’s recall lagged at 74.2 % (missing 8/31), DeviceTotal delivered 100 % recall and zero noise from day zero. FIG-2: Cisco CVE coverage: Bars are counts mapped to IOS 15.9(3)M3 during the window. The callout (+34.8%) shows the uplift vs NVD at that time. FIG-3: Cisco recall on IOS 15.9(3)M3: Recall = TP/(TP+FN) on the correct firmware. NVD’s 74.2% vs DT’s 100% highlights missed exposures (NVD FN=25.8%) that DT caught. FIG-6: CPE mismatch impact on M3: The single column is 100% of M3’s true CVE set (31). It splits into Correct (7) vs Misassigned (24) → labels at top show Recall 22.6% and FNs 77.4%. Case Study B: JTEKT PC10PE-1616P CVE Discoveries A Japanese client used local intelligence (JVN/JPCERT) to scan its JTEKT PC10PE-1616P device. NVD reported 3 vulnerabilities, which was also confirmed by JVN, leading to an apparent “compliant” status. DeviceTotal’s research uncovered 2 additional CVEs (MTTT261501, MTTT261502), bringing the total to 5 — a 66 % increase over JVN/NVD. Public databases offered no remediation guidance, leaving high-severity risks unaddressed; DeviceTotal delivered vendor-verified fixes and full operational context immediately. FIG-7: This graph shows the jump from 3 to 5 vulnerabilities, highlighting DeviceTotal’s ability to reveal hidden vulnerabilities. Case study C — Uncovering a Fortinet FortiGate 200F (FortiOS 7.0.16) Missing CVE For FortiOS 7.0.16, DeviceTotal found 24 CVEs versus NVD’s 23 — a 4.3 % uplift. Notably, CVE-2025-22862, disclosed by Fortinet on June 10, 2025, still had no entry in NVD as of late July, yet DeviceTotal surfaced it immediately with vendor-verified remediation guidance. FIG-4: Fortinet CVE coverage comparison: Two 100% bars: NVD 95.8% covered / 4.2% missed (CVE‑2025‑22862) vs DeviceTotal 100%; +4.3% badge = DT 24 vs NVD 23. This case is not about “just one more CVE.” The point is that CVE‑2025‑22862 remains practically invisible to any NVD‑only workflow. It was reserved by MITRE on Jan 8, 2025 and disclosed by Fortinet on Jun 10, 2025 via FortiGuard/PSIRT, yet NVD still has no entry as of Jul 29, 2025 (“CVE ID Not Found”). That means no NVD CVSS, no CPE mapping, no references — so scanners, SBOM enrichment, and dashboards that depend on NVD won’t see it at all, while DeviceTotal does, because of its vendor-first approach. Read the full case study here.
How DeviceTotal Eliminated False Positives from an NVD CPE Mismatch Before the Fix Went Live

Eight critical Cisco vulnerabilities (CVE‑2025‑20169 through CVE‑2025‑20176) were published without CPE configuration in the NVD, making them invisible to scanners and asset tools that rely on CPE-based matching.
How To Submit Devices To DeviceTotal Community Edition

How To Submit Devices To DeviceTotal Community Edition With DeviceTotal Community Edition, you can evaluate the risk posture of your OT, IoT, network, and security devices — free of charge and without installing anything. You can submit: Up to 3 devices per request 1 request per week Up to 5 requests per month Whether you’re analyzing existing assets or evaluating devices before purchase, Community Edition gives you vendor-verified, firmware-level security intelligence — including vulnerabilities, EoL data, and mitigation options — to help you make confident decisions. Here’s how the submission process works and why each step matters. Step 1: Enter Your Contact Information We ask for your name, email, and company to: Deliver your personalized trial results Follow up with any clarifying questions Ensure your submission is tied to the correct device risk context This information is never shared or used for any purpose beyond your trial experience. Step 2: Select Device Use Context You’ll indicate whether your device is already in use or being evaluated for purchase. This helps us: Understand its operational context Provide recommendations for alternative devices in case of purchase Step 3: Submit Device Information Now you’ll enter as much device data as you have, including: Vendor name Series or model Firmware version (critical for accuracy) SKU number (optional, but useful for deeper matching) After you’ve entered the information, click the “Submit Devices for Evaluation” button. Your evaluation is sent for processing — and within 3 business days, you’ll receive your results. Step 3.1: Submitting Devices You’re Considering for Purchase If you’re submitting a device you’re planning to purchase (instead of one already in use), select the “For Purchase” option. This unlocks an optional recommendation feature that suggests alternative devices from the same category — helping you evaluate options based on security posture, vendor support, known vulnerabilities, and lifecycle status. Ready to Try It? Start FREE Submit up to 3 devices for free and get a full risk report on your IoT, OT, network, and security devices Useful Tip: Make Sure Your Data is Correct The quality of your input directly affects the quality of your results. If you submit only a vendor and model, you’ll receive broad, version-agnostic vulnerabilities If you include the firmware version, we provide: Version-specific CVEs End-of-life data Mitigation/remediation paths Risk scores tied to real-world exploitability This is the same methodology used in our full Intelligence Edition, trusted by service providers and OEMs managing healthcare, OT, IoT, and network device fleets. Your Results: Delivered in JSON Format Your security report will be delivered in JSON — a lightweight, structured format used across modern security and asset management tools. Why JSON? The data we provide is easy to parse with internal tools, making it simple to incorporate into your existing dashboards and reports. It’s designed to be compatible with your current workflows, enabling seamless integration into vulnerability management and asset tracking processes without the need for additional formatting or customization. So, let’s summarize: Easy to parse with internal tools Compatible with dashboards and reports Integrates into existing vulnerability and asset workflows Whether you’re technical or not, JSON gives flexibility. Need help interpreting the results? We’ve got you.
Fortinet Vulnerability Missed by NVD – How DeviceTotal Closed the Gap

Case Study: Fortinet Vulnerability Missed by NVD – How DeviceTotal Closed the Gap A customer operating Fortinet’s FortiGate 200F firewall, firmware version 7.0.16, relied on conventional vulnerability intelligence tools, including NVD, to evaluate the security posture of their network. Their internal compliance processes showed a missed vulnerability as a false negative, which is critical and doesn’t align with the vendor’s official publication on this device. This false sense of security nearly resulted in a major exposure. The DeviceTotal Advantage Without DeviceTotal With DeviceTotal ⚠️ Missed vulnerability as a false negative ✅ Flags CVE-2025-22862 matched to FortiGate 200F ⚠️ Patching opportunity overlooked ✅ Remediation guidance provided – as pet Fortinet security advisory ⚠️ Compliance report misaligned with vendor data ✅ DeviceTotal also recommended on the latest firmware version ⚠️ Exposure to breach due to blind spot ✅ Risk was closed before exposure, with accurate device risk updated daily The Security Gap Device in Use: FortiGate 200F Firmware: 7.0.16 Search Source: NVD Result: No mention of Fortinet or FortiGate products on the NVD at the time of evaluation, and at the time of writing. The Reality Found by DeviceTotal DeviceTotal’s intelligence layer flagged CVE-2025-22862 as relevant to FortiGate 200F, pulling data directly from the official Fortinet advisory:Fortinet PSIRT Advisory The vulnerability does impact FortiGate 200F running firmware version 7.0.16 The issue was disclosed under FG-IR-24-385 Risk rating: CVSS score 6.3 NVD did not associate this CVE with Fortinet at the time of review, and is missing at the time of writing this case study Outcome Thanks to DeviceTotal, the security team was alerted before exploitation, allowing them to: Patch the vulnerability proactively Update asset risk scores accurately Ensure compliance with internal controls and third-party audits This case underscores that NVD alone is not reliable for vulnerability coverage — especially in multi-vendor, high-stakes environments. DeviceTotal closed the intelligence gap, matching the CVE accurately and delivering remediation paths overlooked by public sources. Why It Matters? DeviceTotal’s intelligence engine monitors not only NVD, but: Official vendor advisories Non-reporting vendors Zero-day alerts Enriched private and classified feeds This enables full-spectrum coverage with: Daily intelligence updates Risk scoring matched to specific firmware versions Visibility across IoT, OT, network, and security devices Mitigation paths even when NVD is incomplete or incorrect
Navigating Cyber Risks in the Era of IoT and Emerging Technologies

Navigating Cyber Risks in the Era of IoT and Emerging Technologies The rapid evolution of technology has opened up incredible opportunities for innovation and connectivity, but it has also created a labyrinth of new cybersecurity challenges. From the explosion of IoT devices to the intricate vulnerabilities in Operational Technology (OT), networks, and critical infrastructure, organizations must navigate an ever-expanding digital threat landscape. IoT: The Double-Edged Sword By 2025, the number of IoT devices worldwide is expected to surpass 75 billion, creating vast opportunities for connectivity and automation. However, this explosion of devices also introduces significant risks. Many IoT devices are deployed with minimal security protections, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. These vulnerabilities pose privacy risks, as IoT devices often collect vast amounts of personal data, offering attackers a treasure trove of sensitive information if breached. The sheer number of devices makes securing them a monumental task. As organizations adopt IoT solutions, it becomes crucial to integrate robust security measures into every stage of device deployment and operation. OT and Critical Infrastructure: The Stakes Are Higher The integration of OT systems with IT networks has created a new frontier for cybersecurity challenges. Critical infrastructure sectors—such as energy, water, and transportation—rely on OT systems that are increasingly connected. While this interconnectedness enhances efficiency, it also magnifies risks. A breach in one OT system could cascade across interconnected networks, potentially disrupting vital services. Zero-trust architectures and self-healing networks are becoming essential tools to protect OT environments. These technologies not only minimize the risk of breaches but also ensure operational continuity in the face of increasingly sophisticated attacks. Network Vulnerabilities in the 5G and Edge Computing Era Emerging technologies like 5G and edge computing are transforming how data is processed and transmitted. While these advancements enable faster connectivity and decentralized data processing, they also expand the attack surface for cyber threats. Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in these networks to disrupt services or steal sensitive data. The complexity of supply chains in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) further exacerbates network risks. From tampered components to software vulnerabilities, supply-chain security has become a critical area of concern. Implementing zero-trust frameworks and tamper-proof verification mechanisms is essential to mitigating these threats. The Future: AI and Quantum Risks The rise of artificial intelligence brings new challenges, such as adversarial attacks and data poisoning. Meanwhile, quantum computing looms as a potential disruptor of traditional encryption methods. Some actors are already harvesting encrypted data, anticipating a future where quantum computing could decrypt it. To combat these emerging threats, organizations must invest in quantum-resistant cryptography and AI-driven security tools. Staying ahead of these challenges requires a proactive approach to innovation and resilience. Building a Resilient Future Addressing these complex risks requires a multi-faceted approach. Organizations must: Secure IoT Ecosystems: Deploy devices with built-in security features and continuously monitor their vulnerabilities. Protect OT Systems: Invest in zero-trust architectures and resilience technologies to safeguard critical infrastructure. Fortify Networks: Enhance supply-chain security and prepare for threats to decentralized networks. Embrace Innovation: Adopt AI-driven tools and quantum-resistant cryptography to stay ahead of emerging challenges. Collaborate Globally: Work with regulatory bodies and international organizations to create adaptable security standards. By acknowledging these risks and proactively addressing them, businesses can navigate the cybersecurity challenges of this rapidly changing technological landscape. The road ahead may be complex, but with the right tools and strategies, resilience is within reach. Thank you, [email protected] today! Schedule your free trial today and see how DeviceTotal can protect your network from IoT and OT vulnerabilities.
DeviceTotal Empowers Healthcare Providers to Meet Regulatory Standards and Protect Medical Devices Against Cyber Threats

DeviceTotal Empowers Healthcare Providers to Meet Regulatory Standards and Protect Medical Devices Against Cyber Threats In today’s healthcare industry, the increasing reliance on connected medical devices, such as infusion pumps, imaging systems, and patient monitors, has introduced a new layer of vulnerability to cyber threats. As these devices become integrated into hospital networks, ensuring their cybersecurity is not just important for operational continuity but essential for patient safety and regulatory compliance. The Growing Need for Medical Device Cybersecurity and How DeviceTotal Delivers Protection Cyberattacks on medical devices can disrupt critical care, expose sensitive patient data, and lead to financial and reputational damage for healthcare providers. This has led to a growing emphasis on medical device cybersecurity from regulatory bodies around the world, with standards such as the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act (PMD Act) in Japan and GDPR in the European Union. DeviceTotal addresses these concerns by offering healthcare providers a comprehensive, AI-powered platform that helps secure medical devices and network environments. The platform enables real-time vulnerability assessments, risk management, and compliance with regulatory standards. DeviceTotal’s solution provides healthcare organizations with the tools they need to safeguard their devices, protect sensitive data, and meet critical regulatory requirements. Key Regulatory Standards Addressed by DeviceTotal Regulatory bodies are implementing stricter requirements to ensure the security of medical devices, IoT, and OT systems. For example, the PMD Act in Japan emphasizes risk management for medical devices, while the Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) mandates data security in healthcare settings. DeviceTotal’s solutions align with these frameworks, offering healthcare providers a way to proactively manage vulnerabilities and ensure compliance. Unique Advantages of DeviceTotal Comprehensive Device Coverage: DeviceTotal supports all manufacturers in the market, providing visibility into every device, no matter the vendor. Accurate Threat Intelligence: DeviceTotal continuously updates its cyber threat intelligence database with precise, vendor-specific data, ensuring healthcare providers have access to the latest vulnerabilities and mitigation strategies. Lifecycle Management: The platform offers End-of-Life (EOL) data and updates, helping organizations plan for future upgrades and manage device lifecycles. Contextual Prioritization: By considering vendor-specific metrics and CISA recommendations, DeviceTotal helps healthcare providers prioritize and address the most critical vulnerabilities first. Detailed Remediation Guidance: The platform provides patch information, mitigation actions, and cost-effectiveness insights, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions and reduce security risks. By leveraging DeviceTotal’s platform, healthcare organizations can protect their critical assets, ensure regulatory compliance, and create a secure healthcare environment. In an industry where patient safety and data protection are paramount, DeviceTotal empowers healthcare providers to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. For more detailed insights on this topic, download our latest whitepaper – https://devicetotal.com/case-studies/ Thank you,[email protected] today! Schedule your free trial today and see how DeviceTotal can protect your network from IoT and OT vulnerabilities.
Hezbollah’s Pager Attack: A Defining Moment for Global Device Security
Hezbollah’s Pager Attack: A Defining Moment For Global Device Security In today’s fast-paced world of cyber warfare, few incidents have highlighted the vulnerabilities of connected devices more clearly than the groundbreaking cyber attack on Hezbollah’s pagers. This sophisticated operation, led by Israel, exposed critical security gaps in connected devices, marking a pivotal moment for the entire cybersecurity landscape. While the headlines focused on the immediate impacts of the attack, the event also ignited a global awareness of the looming risks associated with unprotected connected devices, positioning Israel as a key player in the world of cybersecurity. Disrupting Hezbollah’s Communications: A Case Study in Cyber Warfare On September 17th, a decisive cyber strike remotely disabled thousands of pagers used by Hezbollah operatives in Lebanon and Syria. This first strike was followed by the destruction of Hezbollah’s broader communication network the next day. The impact? Significant disruption to Hezbollah’s operational capabilities, resulting in casualties and widespread damage. This operation was a masterclass in combining cyber warfare with physical sabotage. It involved two key tactics: Supply Chain Intervention: Explosive components were covertly introduced into Hezbollah’s pagers during their distribution, transforming everyday communication devices into deadly weapons. Pager Network Intrusion: Israeli cyber units exploited vulnerabilities in Hezbollah’s pager network, gaining remote control of the devices and triggering the embedded explosives with precise timing. This attack demonstrated the urgent need for robust device security, particularly as connected devices become increasingly embedded in critical infrastructures globally. A Global Wake-Up Call for IoT and Device Security The attack on Hezbollah’s pagers sent shockwaves through the cybersecurity world, underscoring the dangers posed by vulnerable connected devices. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), billions of devices—from medical equipment to industrial systems—are now connected to global networks. The lesson is clear: even the most ordinary devices can be exploited as weak points in a broader security ecosystem. Israel’s Leadership in Cybersecurity Innovation Israel has long been recognized as a leader in cybersecurity innovation, a status cemented by its ongoing need to defend against a multitude of threats. The successful operation against Hezbollah not only showcased Israel’s capabilities but also solidified its leadership in device security, particularly in the IoT and Operational Technology (OT) sectors. As the number of connected devices is projected to exceed 75 billion by 2025, Israel’s cybersecurity innovations remain at the forefront of protecting these devices from increasingly complex threats. Key Trends Shaping the Future of Device Security Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the landscape of IoT and device security: AI-Driven Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will play a critical role in identifying and responding to cyber threats in real-time. Zero-Trust Architecture: This model, where every device must be verified before gaining network access, will become standard practice. Enhanced Endpoint Protection: Sophisticated attacks will drive a stronger focus on securing the endpoints of connected devices across various industries. Supply Chain Security: As seen in the Hezbollah pager attack, supply chain security will be essential to prevent the introduction of compromised devices. Regulatory Compliance: Governments will implement stringent cybersecurity regulations, pushing organizations to adopt more comprehensive device security solutions. DeviceTotal: Leading the Charge in Securing Connected Devices At DeviceTotal, we recognize the challenges of securing connected devices in a rapidly evolving threat landscape. Our platform provides unparalleled visibility into device vulnerabilities, offering actionable strategies to mitigate risks across IoT and OT environments. With our advanced risk assessments and remediation solutions, we empower organizations to address vulnerabilities proactively. DeviceTotal’s platform goes beyond identifying risks—it helps organizations future-proof their security by providing vendor-verified intelligence, continuous monitoring, and actionable steps to secure connected devices. As the global demand for device security grows, DeviceTotal stands at the forefront, offering the tools necessary to safeguard organizations from the increasingly sophisticated cyber threats of tomorrow. Take Action Today The Hezbollah pager attack was a stark reminder of the urgency surrounding device security. Now is the time for organizations to take proactive steps to secure their connected infrastructure: Evaluate Your Security Posture: Identify potential vulnerabilities in your devices and take immediate action to address them. Partner with DeviceTotal: Our comprehensive platform offers real-time threat intelligence and mitigation strategies tailored to your specific needs. Future-Proof Your Security: Stay ahead of evolving threats by adopting advanced technologies that protect your devices today and in the future. For more detailed insights on this topic, download our latest whitepaper – https://devicetotal.com/case-studies/ Schedule your free trial today and see how DeviceTotal can protect your network from IoT and OT vulnerabilities.
Eliminate Risks and Challenges in EDR, Vulnerability, and Device Management Solutions

Eliminate Risks and Challenges in EDR, Vulnerability, and Device Management Solutions In the rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations face challenges with vulnerability management and device management solutions. This analysis explores three key domains where these solutions face hurdles that can only be overcome with DeviceTotal’s unique security data. 1. Incomplete Coverage and limited Platform Support 2. Visibility Gaps and complete Device Discovery 3. Complexity in Unmanaged Devices The result is a security blind spot, leaving organizations vulnerable to potential threats originating from unmanaged endpoints. Meet DeviceTotal DeviceTotal goes beyond conventional security solutions by employing cutting-edge AI and machine learning technology to collect security information directly from vendors’ websites and advisories. While many other solutions rely predominantly on the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) for their data, DeviceTotal takes a more proactive and comprehensive approach to provide its clients with full asset security intelligence coverage, regardless of technology, vendor, or industry. DeviceTotal provides a range of capabilities to gain comprehensive visibility, manage vulnerabilities, prioritize software updates, assess risks, ensure compliance, and make informed decisions regarding network, security, IoT, and OT device security and management. Utilizing DeviceTotal comes with no risk, offering rapid, high-value results, as it eliminates the need for installations in the client’s network. Easily integrate your assets directly from your CMDB or input them manually, and witness instant visibility into the security posture, along with readily available mitigation options.Here’s an overview of these capabilities: Gain Visibility of IoT, OT, and Unmanaged Devices DeviceTotal offers the capability to achieve comprehensive visibility into the Internet of Things (IoT), Operational Technology (OT), and unmanaged devices within the network. This ensures organizations have a complete understanding of their device landscape, enhancing control and security. Reduce Vulnerabilities Proactively identify vulnerabilities present in devices and prioritize by risk, manage remediation efforts, and reduce the risk of exploitation. Manage, Prioritize, and Apply Software Updates DeviceTotal enables organizations to manage and prioritize software updates for their devices effectively. This feature ensures timely application of critical security patches, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and enhancing overall security Patch Management DeviceTotal provides timely notifications for software updates and new vulnerabilities, keeping organizations informed about the latest patches and vulnerabilities relevant to their devices. This enables prompt action to leverage automation to ensure and maintain a secure environment. Receive Actionable Insights and Workarounds DeviceTotal understands the complex and sometimes disruptive nature of updates, and provides workaround recommendations, supplied by the vendors, ensuring critical assets will remain secure until updates are scheduled. Streamline, Achieve, and Maintain Compliance Enables organizations to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards and industry frameworks. DeviceTotal For ICS/OT DeviceTotal is an ideal cybersecurity solution for the industrial market, particularly in Operational Technology (OT) environments, where the demand for robust security is paramount. Its unique feature of requiring no integration and installation is critical in the context of OT, where minimizing disruptions is essential. Beyond this, DeviceTotal offers meticulous vulnerability analysis, eliminating ambiguity in reports. Its comprehensive and accurate vulnerability database fortifies industrial systems against potential threats. The platform’s essential workaround capability enhances its value, ensuring effective mitigation planning. Gain Real Complete Visibility and Eliminate Risks Investigating the functionalities and attributes of leading EDRs and vulnerability management solutions today reveals a common deficiency in visibility and risk management for unmanaged devices. Moreover, these solutions exhibit limitations in delivering comprehensive network support, leading to blind spots and potential security breaches. Integrations with DeviceTotal bring new value to the market. By leveraging DeviceTotal’s comprehensive data, organizations can bridge information gaps, ensuring well-informed decision-making processes. DeviceTotal goes beyond the ordinary, offering a depth of coverage that outshines traditional databases. Every vulnerability, for every network, IoT, and OT device – we’ve got you covered. Enhanced Visibility: Don’t settle for partial insights. DeviceTotal enhances your visibility, ensuring you see the complete picture of your digital landscape. No surprises, just proactive cybersecurity. Unmatched Support for Unmanaged Devices: DeviceTotal’s advanced capabilities make managing unmanaged devices a breeze. Elevate your security posture effortlessly. Schedule your free trial today and see how DeviceTotal can protect your network from IoT and OT vulnerabilities.
